Prepare
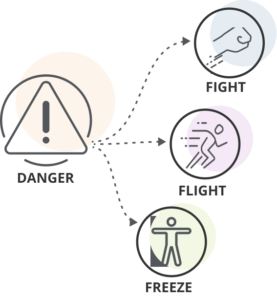
The first step in creating a culture that supports behavior is to prepare. The work of behavior support must be rooted in safety. This section first outlines the connection between safety and behavior, and helpful resources to review before getting started. You will then be ready to develop a deeper understanding of what behavior support means, and how to move forward.
Before You Begin
What is Behavior?
What is Behavior Support?
Getting Started
Head over to Assess from here to determine which resources and tools will be most helpful to you.